Currently Empty: £0.00
mbakr
- November 21, 2025
- Comment 0
ABSTRACT
Hair loss is a multifactorial condition influenced by genetics, hormones, inflammation, nutritional factors, and environmental triggers. Modern aesthetic medicine provides a range of minimally invasive and regenerative treatments capable of restoring hair density, improving follicular health, and enhancing patient confidence. This module presents an in-depth clinical overview of common types of hair loss, diagnostic pathways, and evidence-based treatment modalities including Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP), mesotherapy, low-level laser therapy (LLLT), exosomes, polynucleotides, microneedling, and combination treatment protocols. It equips practitioners with the scientific foundation and practical guidelines needed for effective and safe hair restoration.
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
After completing this module, learners will be able to:
- Identify and diagnose common types of hair loss.
- Understand the biological mechanisms of PRP, mesotherapy, LLLT, exosomes, and regenerative therapies.
- Develop structured treatment protocols tailored to patient needs.
- Recognize contraindications and high-risk cases.
- Manage complications and set realistic patient expectations.
- INTRODUCTION
Hair loss affects both men and women across various age groups and can significantly impact psychological well-being. Advanced aesthetic medicine provides non-surgical interventions that promote:
- Follicle regeneration
- Improved microcirculation
- Reduction of inflammation
- Activation of dormant follicles
- Hair shaft strengthening
Proper diagnosis and a multimodal approach produce optimal outcomes.
- TYPES OF HAIR LOSS & DIAGNOSTIC WORK-UP
2.1 Androgenetic Alopecia (AGA)
Most common type.
Characterized by:
- Miniaturization of hair follicles
- Shortened anagen phase
- Genetic and hormonal influence (DHT sensitivity)
Typical patterns:
- Male pattern: temples & crown
- Female pattern: diffuse thinning over crown
2.2 Telogen Effluvium (TE)
Trigger-induced shedding.
Causes:
- Stress
- Fever/illness
- Postpartum
- Medications
- Nutrient deficiencies
Reversible when trigger addressed.
2.3 Alopecia Areata
Autoimmune disorder
Patchy hair loss
May require combination therapy with dermatology oversight.
2.4 Scarring Alopecia
Permanent destruction of follicles.
Referral to dermatologist required.
2.5 Diagnostic Evaluation
Clinical Evaluation
- Hair-pull test
- Pattern mapping
- Dermatoscopy (trichoscopy)
Laboratory Investigation
Recommended tests:
- Ferritin
- Vitamin D
- Thyroid profile
- Zinc levels
- Hormone panel (PCOS, androgens if indicated)
Accurate diagnosis guides correct treatment selection.
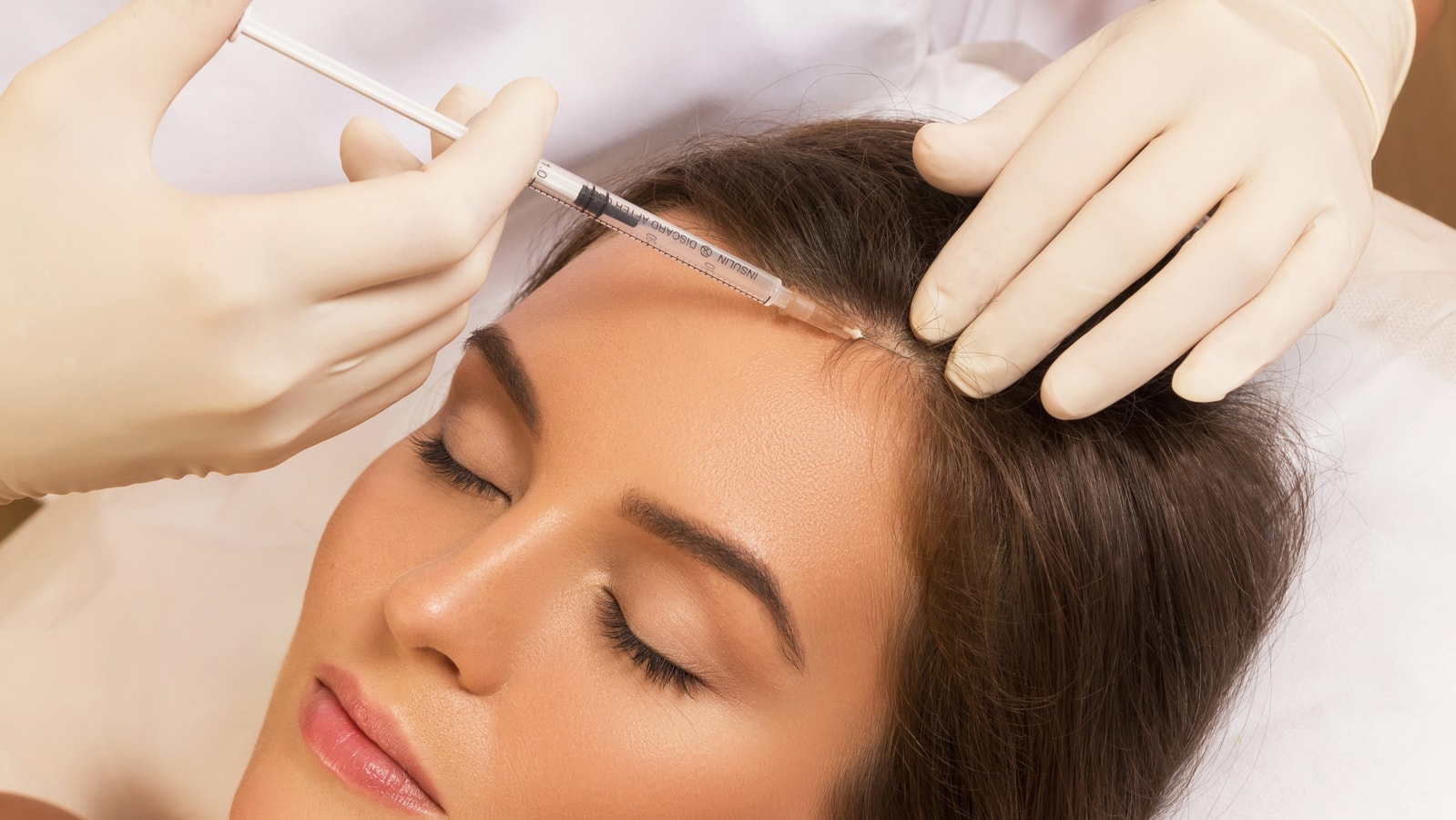
- PLATELET-RICH PLASMA (PRP)
3.1 Mechanism of Action
PRP contains growth factors including:
- PDGF
- TGF-β
- VEGF
- EGF
These promote:
- Angiogenesis
- Prolonged anagen phase
- Reduced inflammation
- Follicular regeneration
3.2 PRP Preparation
Factors influencing quality:
- Centrifuge type (single vs double spin)
- Platelet concentration
- Use of anticoagulants
Ideal concentration: 4–5x baseline platelet count
3.3 Clinical Protocol
- Sessions: every 3–6 weeks for 3–6 sessions
- Maintenance: every 3–6 months
- Injection depth: 1–3 mm intradermal
- Method: nappage or point-by-point
3.4 Indications
- Androgenetic alopecia (early–moderate)
- Telogen effluvium (as adjunct)
- Hair quality improvement
3.5 Advantages
- Autologous
- Safe
- Minimal downtime
3.6 Limitations
- Requires multiple sessions
- Not effective in advanced miniaturization
- Technique-dependent
- MESOTHERAPY FOR HAIR LOSS
4.1 Mechanism of Action
Mesotherapy delivers microinjections of active ingredients into the dermis.
Formulas commonly include:
- Vitamins (Biotin, B-complex)
- Amino acids
- Peptides
- Hyaluronic acid
- Minerals
- DHT blockers
Mechanisms:
- Improved blood flow
- Nutrient delivery
- Reduced inflammation
- Follicle stimulation
4.2 Treatment Protocol
- Weekly sessions x 4–8
- Maintenance every 1–3 months
- Injection technique: microbolus or nappage
4.3 Indications
- Telogen effluvium
- Early androgenetic alopecia
- Hair shaft strengthening
- LOW-LEVEL LASER THERAPY (LLLT)
5.1 Mechanism
LLLT stimulates mitochondria in follicular cells.
Effects include:
- ATP production
- Increased blood circulation
- Prolonged anagen phase
- Reduced inflammation
5.2 Clinical Use
- 2–3 sessions per week
- Helmet, comb, or panel devices
5.3 Indications
- AGA (male & female)
- Diffuse thinning
- Maintenance therapy
- MICRONEEDLING FOR HAIR RESTORATION
6.1 Mechanism
Microneedling creates controlled micro-injuries:
- Increases growth factor release
- Enhances topical penetration
- Stimulates Wnt/β-catenin pathway
- Supports dermal papilla activation
6.2 Protocol
- Needle depth: 0.6–1.5 mm
- Frequency: every 1–2 weeks
- Often combined with PRP, peptides, or minoxidil
- REGENERATIVE THERAPIES
7.1 Exosomes
Extracellular vesicles containing:
- Growth factors
- Cytokines
- mRNA
- miRNA
Benefits:
- Reduce inflammation
- Activate stem cells
- Restore follicular microenvironment
7.2 Polynucleotides (PN / PDRN)
Mechanism:
- Enhance tissue repair
- Improve blood flow
- Reduce oxidative stress
- Support hair density
7.3 Stem Cell-Based Therapies
Include:
- Adipose-derived stem cells
- Autologous cellular concentrates
Work by regenerating follicular niche.
7.4 Combination Regenerative Protocols
Examples:
- Exosomes + microneedling
- PRP + PN
- PRP + microneedling + LLLT
Combination therapy delivers superior outcomes.
- TOPICAL & SYSTEMIC ADJUNCTS
8.1 Topical Minoxidil
- Vasodilator
- Increases anagen duration
Forms:
- 2%, 5%,
8.2 Finasteride / Dutasteride
5α-reductase inhibitors
Used in male AGA (and selected female cases)
8.3 Multivitamins & Supplements
Beneficial in deficiency-related cases:
- Iron
- Vitamin D
- Zinc
- Biotin
- COMBINATION APPROACHES
9.1 Examples of Integrated Treatment Plans
Male AGA (Early Stage)
- PRP every 4 weeks x 3
- Oral finasteride
- Minoxidil topical
- LLLT 2–3x weekly
Female Pattern Hair Loss
- PRP x 3
- Mesotherapy with peptides
- Topical minoxidil
- Address hormonal imbalances
Telogen Effluvium
- Mesotherapy
- Nutritional correction
- Stress management
- Maintained with PRP or LLLT
Advanced AGA
- Combined PRP + exosomes
- Microneedling every 2 weeks
- Consideration of transplantation
- SAFETY, RISKS & COMPLICATION MANAGEMENT
10.1 PRP
- Bruising
- Mild pain
- Swelling
- Infection (rare with sterile technique)
10.2 Mesotherapy
- Allergic reactions (depending on formula)
- Swelling
- Tenderness
- Rare nodules
10.3 LLLT
Extremely safe
Occasional headaches or scalp warmth
10.4 Microneedling
- Pinpoint bleeding
- Erythema
- PIH in dark skin if overly aggressive
10.5 Exosomes / PN
- Mild redness
- Temporary sensitivity
- POST-TREATMENT CARE
General recommendations across treatments:
- Avoid sweating for 24 hours
- Avoid hair dye for 48–72 hours
- No heavy exercise for 24 hours
- Use gentle shampoo
- No heat exposure
- Avoid anti-inflammatory medications for 24 hours after PRP
Follow-up every 4–6 weeks is essential for tracking progress and adjusting the plan.
- KEY LEARNING POINTS
- Hair loss requires proper diagnosis before treatment begins.
- PRP is a cornerstone treatment with strong regenerative effects.
- Mesotherapy improves scalp nutrition and complements other therapies.
- LLLT enhances cellular metabolism and supports long-term maintenance.
- Exosomes and PN offer advanced biologic rejuvenation.
- Combination therapy provides superior results over monotherapy.
- Patient education and compliance determine long-term success.